🥇Top ML Papers of the Week
The top ML Papers of the Week (August 7 - August 13)
1). LLMs as Database Administrators - presents D-Bot, a framework based on LLMs that continuously acquires database maintenance experience from textual sources; D-Bot can help in performing: 1) database maintenance knowledge detection from documents and tools, 2) tree of thought reasoning for root cause analysis, and 3) collaborative diagnosis among multiple LLMs. (paper | tweet)
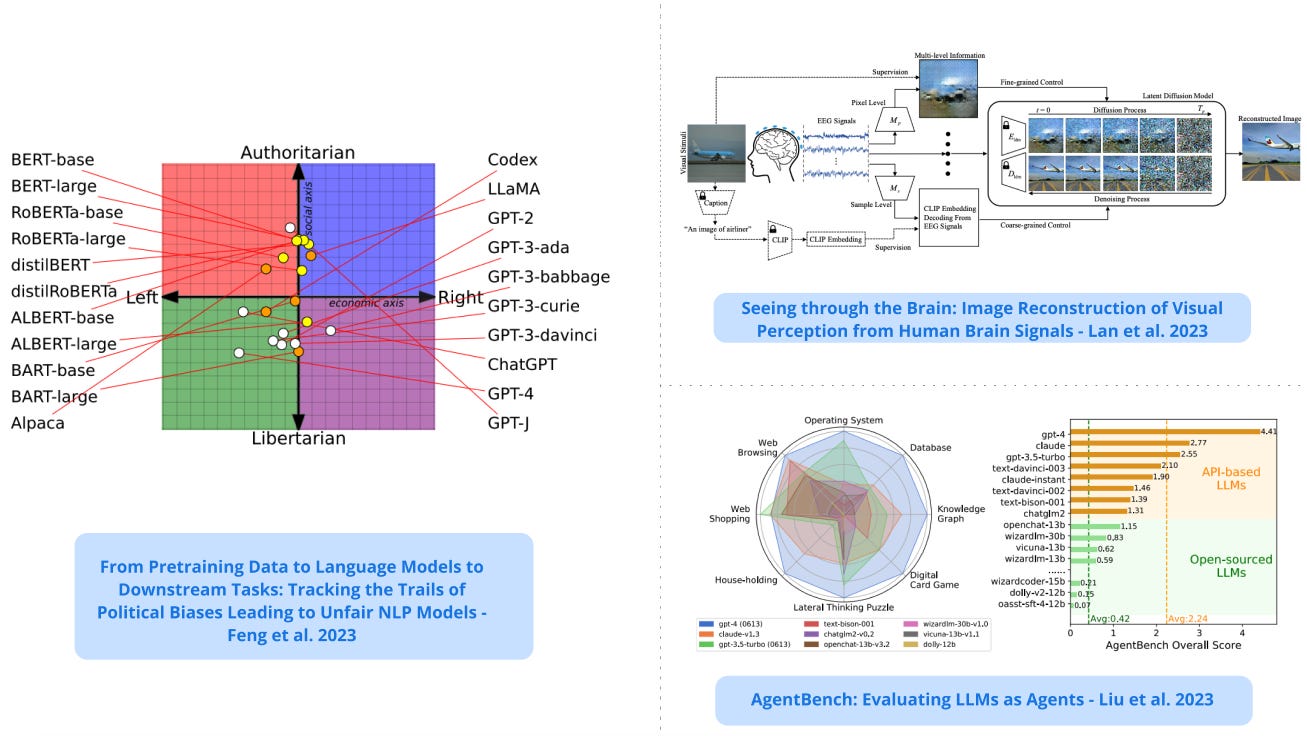
2) Political Biases Found in NLP Models - develops methods to measure media biases in LLMs, including the fairness of downstream NLP models tuned on top of politically biased LLMs; findings reveal that LLMs have political leanings which reinforce existing polarization in the corpora. (paper | tweet)
3). Evaluating LLMs as Agents - presents a multidimensional benchmark (AgentBench) to assess LLM-as-Agent’s reasoning and decision-making abilities; results show that there is a significant disparity in performance between top commercial LLMs and open-source LLMs when testing the ability to act as agents; open-source LLMs lag on the AgentBench tasks while GPT-4 shows potential to build continuously learning agents. (paper | tweet)
4). Studying LLM Generalization with Influence Functions - introduces an efficient approach to scale influence functions to LLMs with up to 52 billion parameters; the influence functions are used to further investigate the generalization patterns of LLMs such as cross-lingual generalization and memorization; finds that middle layers in the network seem to be responsible for the most abstract generalization patterns. (paper | tweet)
5). Seeing Through the Brain - proposes NeuroImagen, a pipeline for reconstructing visual stimuli images from EEG signals to potentially understand visually-evoked brain activity; a latent diffusion model takes EEG data and reconstructs high-resolution visual stimuli images. (paper | tweet)
Sponsor message
DAIR.AI presents a new cohort-based course, Prompt Engineering for LLMs, that teaches how to effectively use the latest prompt engineering techniques and tools to improve the capabilities, performance, and reliability of LLMs. Enroll here.
6). SynJax - is a new library that provides an efficient vectorized implementation of inference algorithms for structured distributions; it enables building large-scale differentiable models that explicitly model structure in data like tagging, segmentation, constituency trees, and spanning trees. (paper | tweet)
7). Synthetic Data Reduces Sycophancy in LLMs - proposes fine-tuning on simple synthetic data to reduce sycophancy in LLMs; sycophancy occurs when LLMs try to follow a user’s view even when it’s not objectively correct; essentially, the LLM repeats the user’s view even when the opinion is wrong. (paper | tweet)
8). Photorealistic Unreal Graphics (PUG) - presents photorealistic and semantically controllable synthetic datasets for representation learning using Unreal Engine; the goal is to democratize photorealistic synthetic data and enable more rigorous evaluations of vision models. (paper | tweet)
9). LLMs for Industrial Control - develops an approach to select demonstrations and generate high-performing prompts used with GPT for executing tasks such as controlling (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) for buildings; GPT-4 performs comparable to RL method but uses fewer samples and lower technical debt. (paper | tweet)
10). Trustworthy LLMs - presents a comprehensive overview of important categories and subcategories crucial for assessing LLM trustworthiness; the dimensions include reliability, safety, fairness, resistance to misuse, explainability and reasoning, adherence to social norms, and robustness; finds that aligned models perform better in terms of trustworthiness but the effectiveness of alignment varies. (paper | tweet)
Reach out to hello@dair.ai if you would like to sponsor the next issue of the newsletter. We can help promote your AI tool, research, or company to ~10K AI researchers and practitioners.