🥇Top ML Papers of the Week
The top ML Papers of the Week (Feb 20 - Feb 26)
This issue highlights the top ML Papers of the Week (Feb 20 - Feb 26).
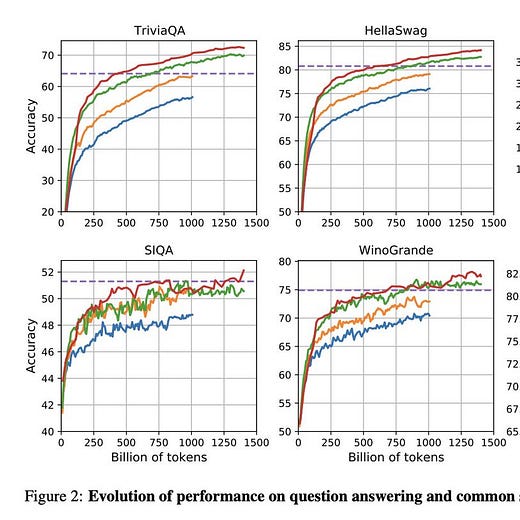
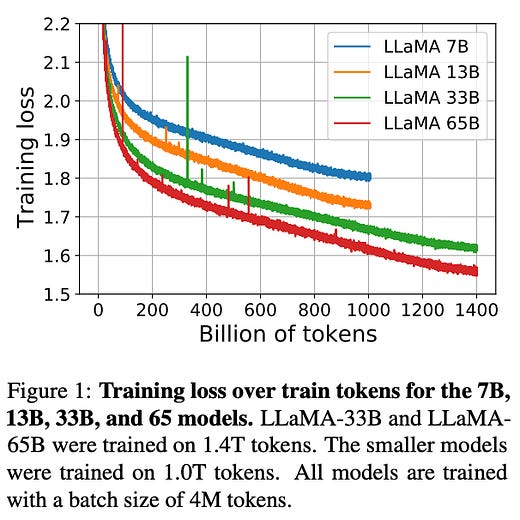
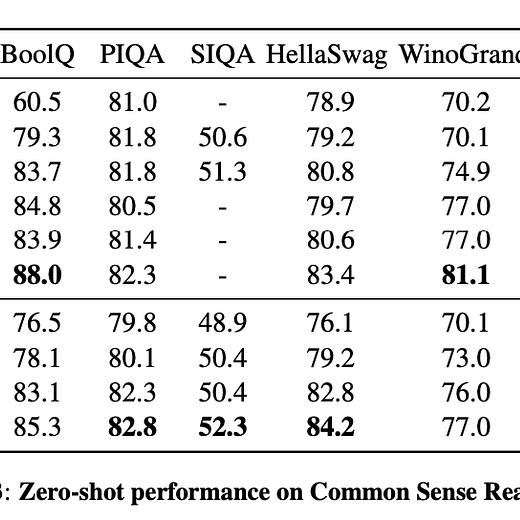
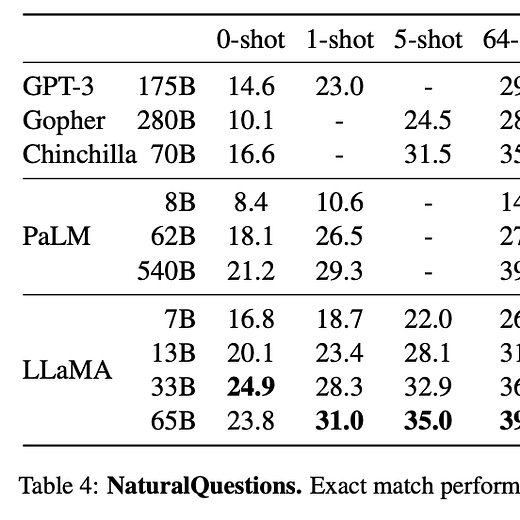
1). LLaMA - a 65B parameter foundation model released by Meta AI; relies on publicly available data and outperforms GPT-3 on most benchmarks despite being 10x smaller. (paper)
2) Composer - a 5B parameter creative and controllable diffusion model trained on billions (text, image) pairs. (paper)
3) Hindsight Instruction Relabeling - an alternative algorithm to train LLMs from feedback; the feedback is converted to instruction by relabeling the original one and training the model, in a supervised way, for better alignment. (paper)
4). Active-Prompt - a prompting technique to adapt LLMs to different task-specific example prompts (annotated with human-designed chain-of-thought reasoning); this process involves finding where the LLM is most uncertain and annotating those. (paper)
5). Modular Deep Learning - a survey offering a unified view of the building blocks of modular neural networks; it also includes a discussion about modularity in the context of scaling LMs, causal inference, and other key topics in ML. (paper)
6). Recitation-Augmented LMs - an approach that recites passages from the LLM’s own memory to produce final answers; shows high performance on knowledge-intensive tasks. (paper)
7). LLMs to Optimize Code - an approach that uses LLMs to suggest functionally correct, performance-improving code edits. (paper)
8). Prompt Injection Threats - a comprehensive analysis of novel prompt injection threats to application-integrated LLMs. (paper)
9). Aligning Text-to-Image Models using Human Feedback - proposes a fine-tuning method to align generative models using human feedback. (paper)
10). MERF - a memory-efficient radiance field representation for real-time view synthesis of large scenes in a browser. (paper)
See you next week for another round of awesome ML papers!