🥇Top AI Papers of the Week
The Top AI Papers of the Week (December 15-21)
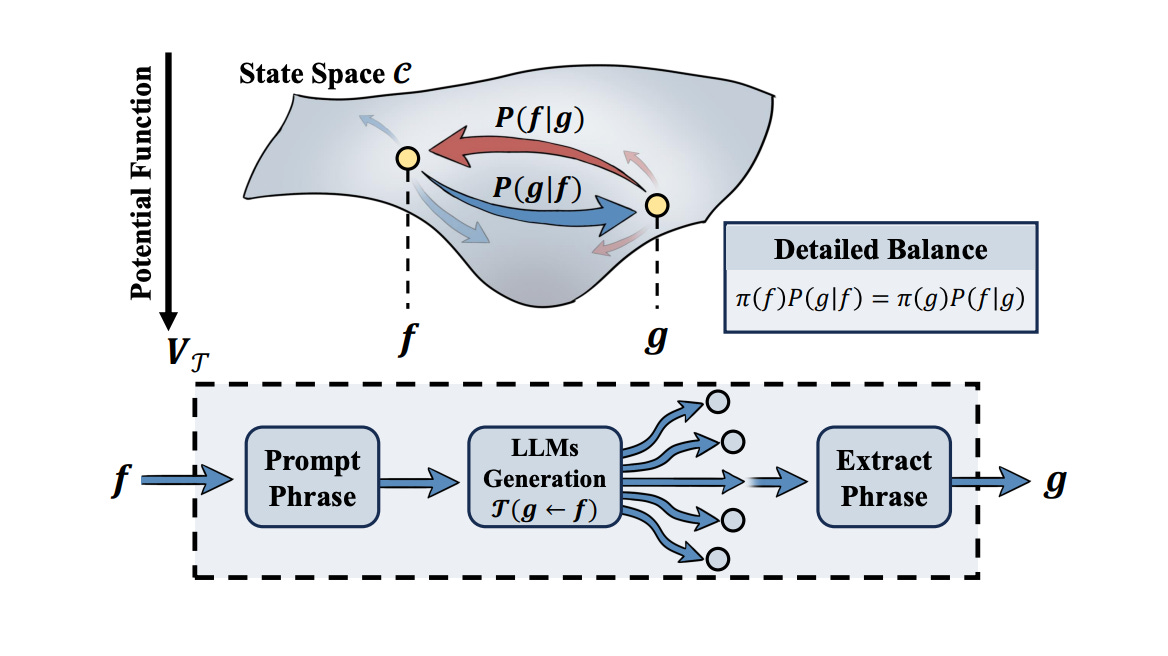
1. Detailed Balance in LLM Agents
Researchers establish the first macroscopic physical law in LLM generation dynamics by applying the least action principle to analyze LLM-agent behavior. They discover statistical evidence of detailed balance in state transitions, suggesting LLMs implicitly learn underlying potential functions rather than explicit rules.
Theoretical framework: Applies statistical mechanics concepts to understand LLM-agent dynamics. The framework transcends specific model architectures and prompt templates.
Detailed balance discovery: By measuring transition probabilities between LLM-generated states, researchers identify balanced properties similar to physical systems at equilibrium.
Implicit learning: Results suggest LLMs may learn underlying potential functions that govern generation, rather than memorizing explicit rule sets from training data.
Why it matters: This interdisciplinary work bridges physics and AI, providing a theoretical foundation for understanding complex AI agent behavior at a macroscopic level independent of implementation details.
Message from the Editor
We are excited to announce our second cohort on Claude Code for Everyone. Learn how to leverage Claude Code for increasing your productivity and vibe coding.
Use coupon code EARLYBIRDCC25 for 25% today. Seats are limited!
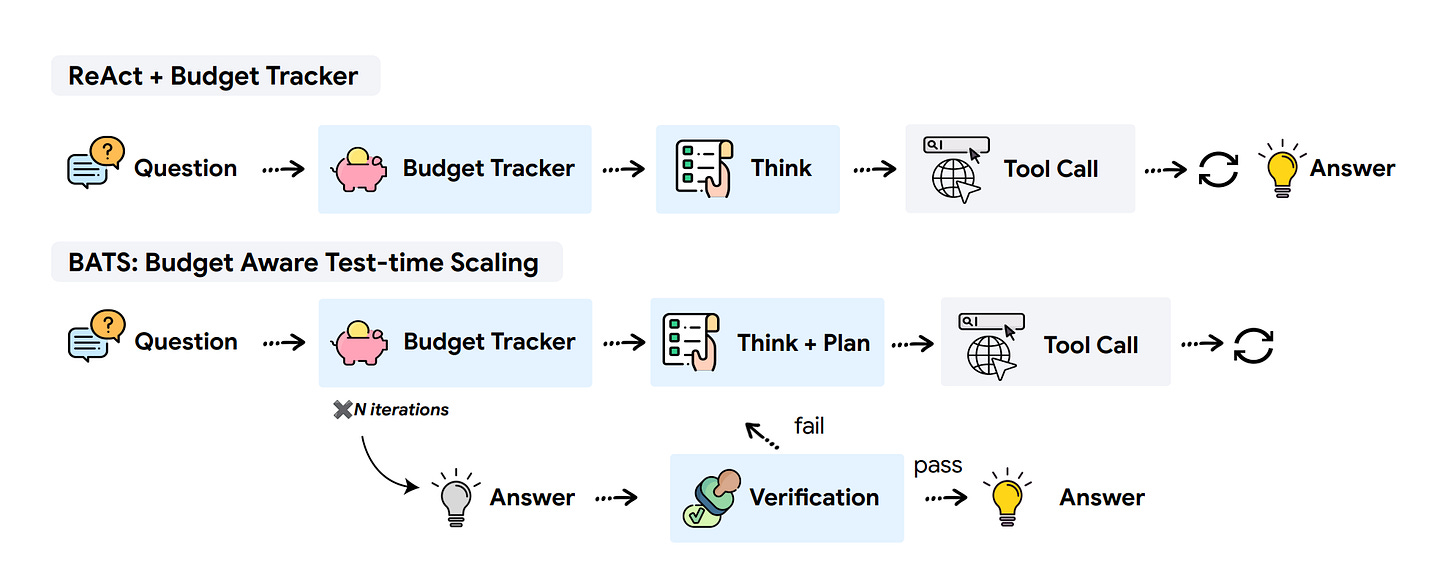
2. Budget Aware Test-time Scaling
Researchers discover that simply expanding tool-call budgets without proper awareness fails to improve agent performance. They introduce BATS (Budget Aware Test-time Scaling), a framework that makes web search agents budget-aware, enabling more strategic resource allocation and pushing the cost-performance Pareto frontier.
Key finding: Increasing token budgets improves LLM performance, but expanding tool-call budgets without awareness yields no improvement. Resource consciousness is essential for effective agent scaling.
Budget Tracker Plugin: A lightweight mechanism that provides agents with continuous awareness of remaining resources, enabling strategic decision-making throughout task execution.
BATS framework: Dynamically adjusts exploration strategy based on remaining capacity - deciding whether to pursue promising leads deeper or explore alternative paths.
Results: Budget-aware approaches produce more favorable scaling curves and systematically improve agent efficiency under computational constraints. First comprehensive study of budget-constrained tool-augmented agents.
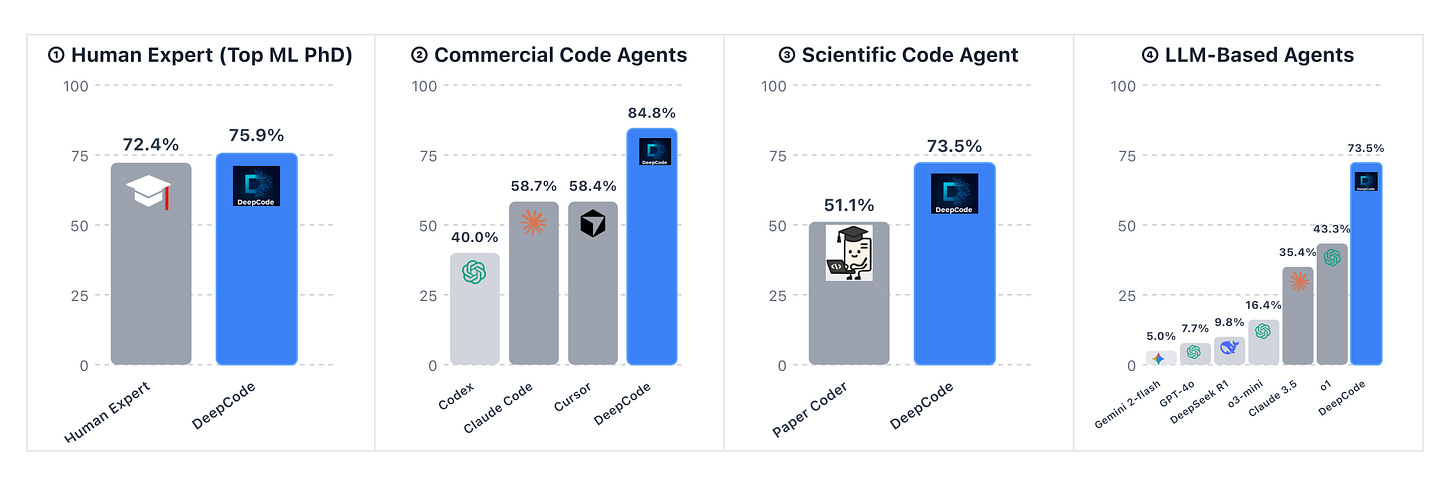
3. DeepCode
DeepCode is a fully autonomous framework for synthesizing complete codebases from scientific papers despite LLM context limitations. It treats repository synthesis as a channel optimization problem, achieving state-of-the-art on PaperBench and outperforming commercial tools like Cursor and Claude Code.
Blueprint distillation: Compresses source documents into structured representations that preserve essential implementation details while fitting within context windows.
Stateful code memory: Maintains structured indexing for organized knowledge across the codebase, enabling coherent multi-file generation.
Retrieval-augmented generation: Injects relevant context conditionally during generation, ensuring each code component has access to necessary dependencies and specifications.
Closed-loop error correction: Iteratively refines generated code through automated testing and debugging, catching and fixing issues autonomously.
4. FrontierScience
OpenAI introduced FrontierScience, a new benchmark measuring AI capabilities for expert-level scientific reasoning across physics, chemistry, and biology. The benchmark consists of over 700 questions created and verified by domain experts, including international olympiad medalists and PhD scientists.
Two evaluation tracks: FrontierScience-Olympiad contains 100 questions designed by olympiad medalists for constrained short-answer reasoning. FrontierScience-Research has 60 open-ended research subtasks graded on 10-point rubrics.
Benchmark results: GPT-5.2 leads with 77% on Olympiad and 25% on Research tasks. Gemini 3 Pro scored 76% on the Olympiad. The Research track shows significant room for improvement.
Expert collaboration: 42 former international medalists (totaling 109 olympiad medals) created Olympiad questions. 45 PhD scientists across quantum electrodynamics, synthetic chemistry, and evolutionary biology developed Research tasks.
Why it matters: As GPQA went from 39% with GPT-4 to 92% with GPT-5.2 in two years, FrontierScience provides harder problems to track progress toward AI-accelerated scientific discovery.
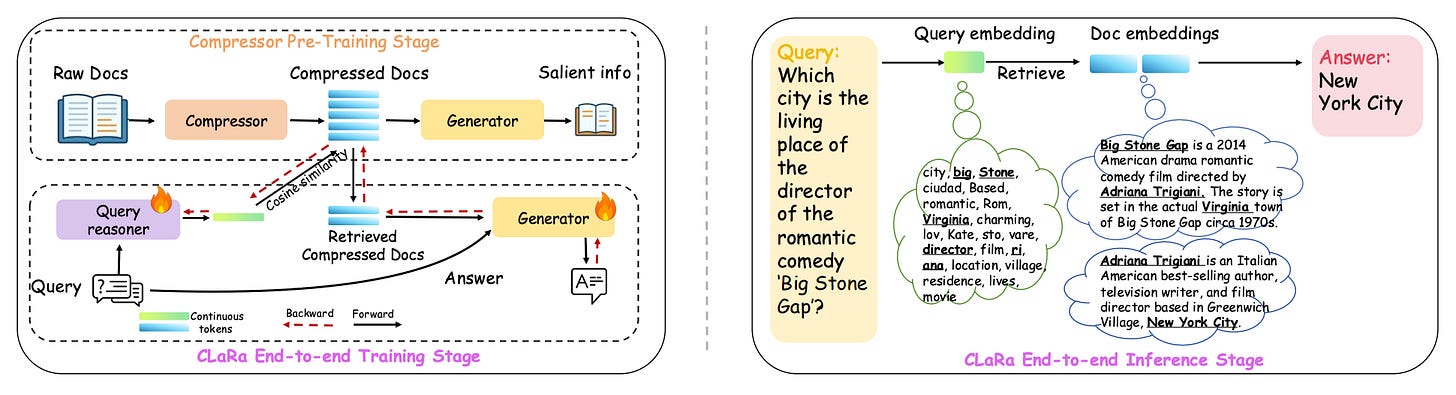
5. CLaRa
CLaRa introduces a unified framework for retrieval-augmented generation that performs embedding-based compression and joint optimization in a shared continuous space. The approach addresses key RAG limitations around long contexts and disjoint retrieval-generation optimization.
SCP data synthesis: Uses question-answer and paraphrase supervision to create semantically rich compressed vectors that remain retrievable for downstream tasks.
End-to-end optimization: Trains the reranker and generator simultaneously using a single language modeling objective. Gradients flow through both modules via a differentiable top-k estimator.
Theoretical grounding: The unified optimization approach theoretically connects retrieval relevance with answer quality, aligning what gets retrieved with what improves generation.
Results: Achieves state-of-the-art compression and reranking performance across multiple QA benchmarks, often surpassing text-based fine-tuned baselines.
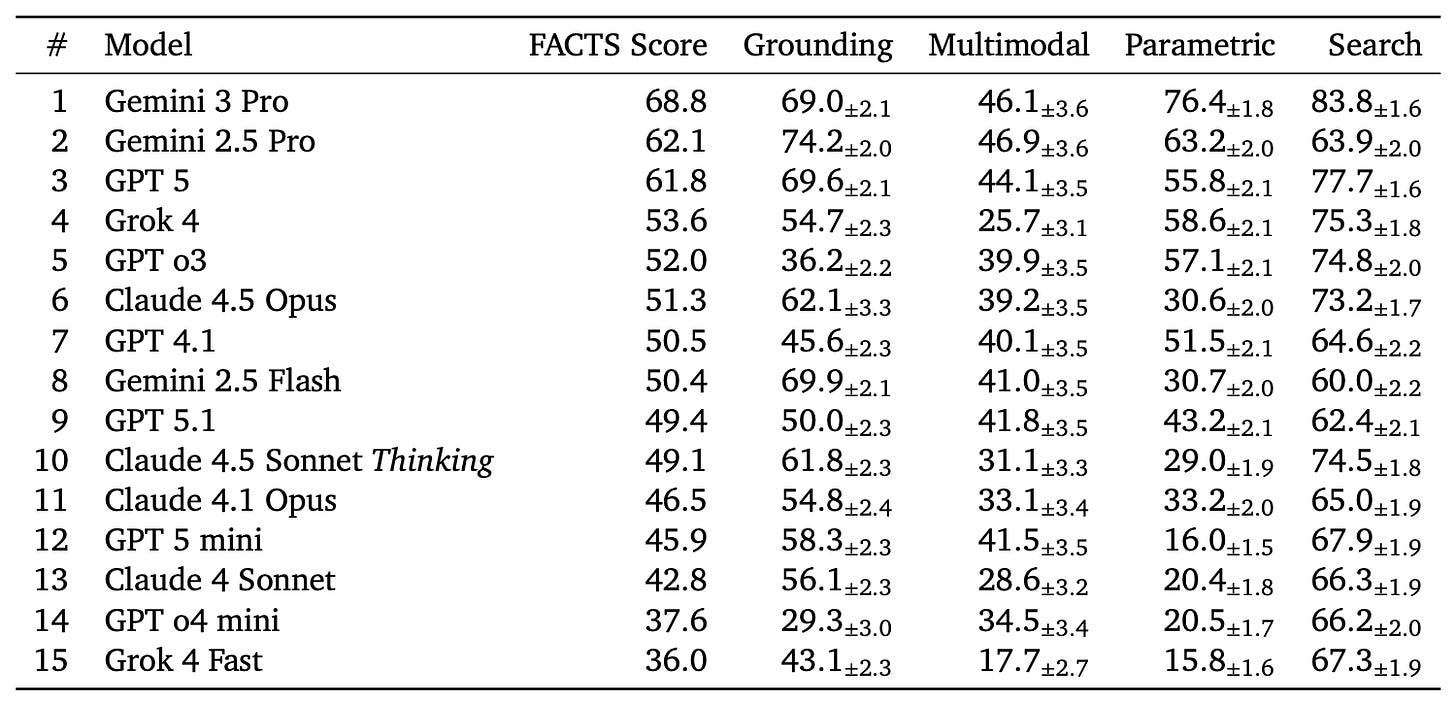
6. FACTS Leaderboard
Google introduces the FACTS Leaderboard, a comprehensive benchmark suite for evaluating LLM factuality across diverse scenarios. The leaderboard aggregates performance across four specialized sub-benchmarks to provide a holistic measure of how accurately models generate factual text.
Four evaluation dimensions: FACTS Multimodal tests visual grounding with world knowledge on image-based questions. FACTS Parametric measures closed-book factoid question answering from internal parameters. FACTS Search evaluates factuality when using search APIs. FACTS Grounding v2 checks if long-form responses align with source documents.
Automated judging system: Each sub-leaderboard uses automated judge models to score responses. The final FACTS Score averages all four components for a balanced assessment. Coverage and No-Contradiction verdicts ensure responses are both complete and accurate.
Current rankings: Gemini 3 Pro leads with 68.8% overall, followed by Gemini 2.5 Pro at 62.1% and GPT 5 at 61.8%. The benchmark reveals trade-offs - Gemini models show higher coverage while GPT models achieve better no-contradiction scores.
Benchmark integrity: The suite includes public and private test splits to prevent overfitting. Hosted on Kaggle, it remains open for new model submissions while maintaining evaluation integrity through hidden test prompts.
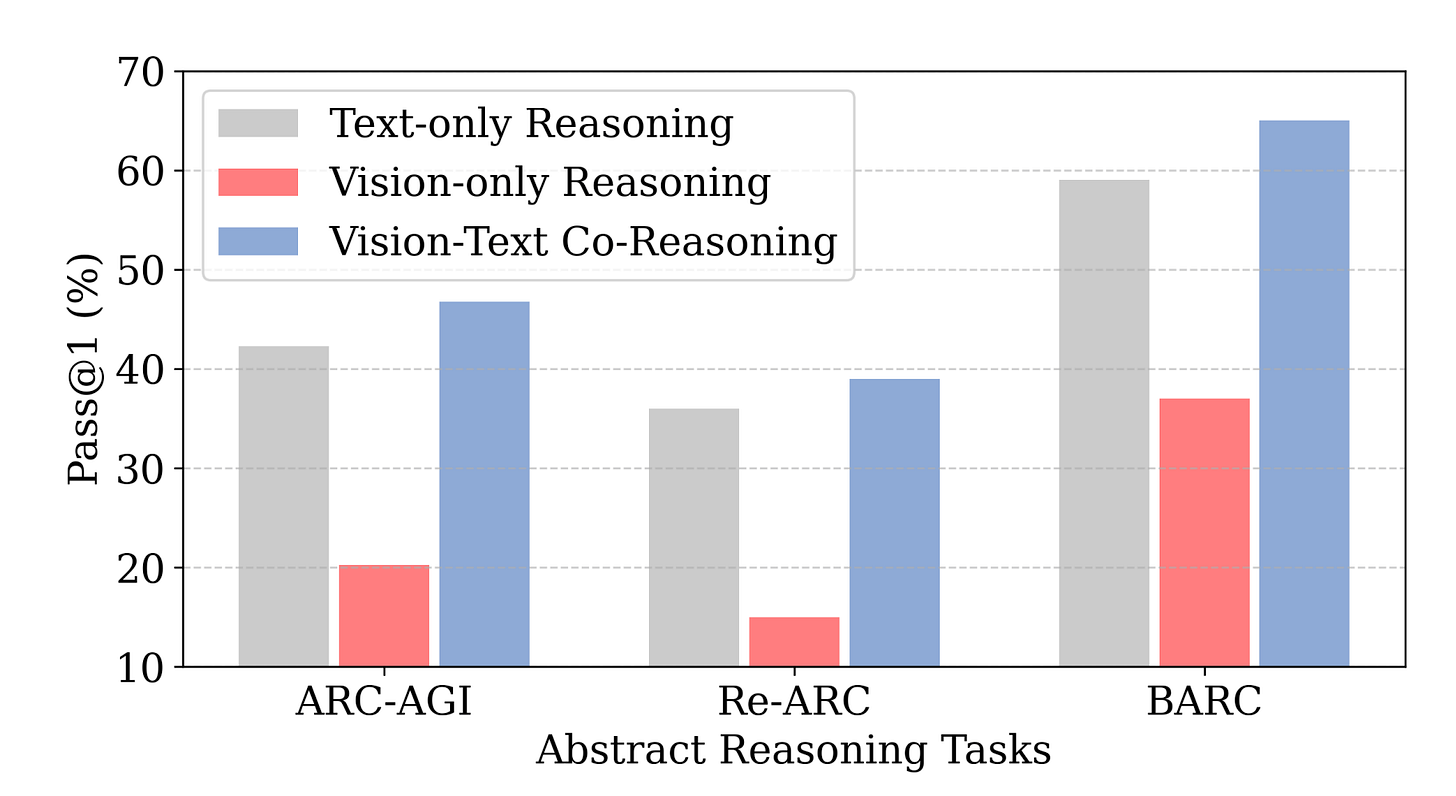
7. Vision-Language Synergy Reasoning
Researchers propose Vision-Language Synergy Reasoning (VLSR), a method that combines visual and textual reasoning to improve performance on ARC-AGI abstract reasoning tasks. The key insight is that vision excels at global pattern abstraction while language specializes in symbolic rule formulation.
Modality strengths: Vision supports pattern recognition and verification across the entire puzzle grid. Language handles precise rule formulation and step-by-step execution of transformations.
VLSR decomposition: The framework assigns subtasks to each modality based on their strengths - visual processing for pattern abstraction, text for symbolic reasoning, and rule application.
Modality-Switch Self-Correction: MSSC uses visual verification to catch errors in text-based reasoning. When text execution fails, the system switches to visual mode to identify and fix mistakes.
Results: Achieves up to 4.33% improvement over text-only baselines on ARC-AGI tasks across multiple foundation models, demonstrating that unifying visual abstraction with linguistic reasoning advances generalizable AI.
8. SHARP
SHARP generates photorealistic novel viewpoints from a single photograph in under one second on standard GPU hardware. The neural network produces a 3D Gaussian representation in a single feedforward pass, enabling real-time rendering for nearby viewing angles. It reduces LPIPS by 25-34% and achieves three orders of magnitude faster synthesis than prior approaches with strong zero-shot generalization.
9. ARTEMIS
Stanford researchers conducted the first head-to-head evaluation of AI agents against human cybersecurity professionals on a live enterprise network with approximately 8,000 hosts. Their multi-agent framework ARTEMIS placed second overall, discovering 9 valid vulnerabilities with 82% accuracy and outperforming 9 of 10 human testers at a fraction of the cost (18 dollars per hour vs 60 dollars per hour for professionals).
10. Stronger Normalization-Free Transformers
Researchers introduce Derf, a simple point-wise function that replaces normalization layers in Transformers. Based on the rescaled Gaussian cumulative distribution function, Derf outperforms LayerNorm, RMSNorm, and Dynamic Tanh across vision, speech, and DNA sequence modeling tasks with improved generalization rather than stronger fitting capacity.